RN vs. BSN: What's the Difference?
Is a BSN worth it? Do I need one to become a nurse? What does the career outlook for both paths look like? What are the salary expectations? Find out the answers to these common questions in this blog.
Since the early 1900s, nurses have played an integral part in healthcare systems all over the world. And today, this is a profession in high demand that is only increasing as each year passes. In fact, by 2028, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates a 12% growth for all registered nurse (RN) positions.
But is it better to be an RN or a BSN? What exactly is the difference? Two excellent questions. If you're entirely new to the terminologies, the differences may surprise you.
While an RN and BSN are similar in the sense that they both relate to nursing, one is a degree and the other is a license.
Can you guess which one is which? In this article, we’ll go through what an RN and BSN are, what the differences are, and much more.
An RN, or Registered Nurse, is a licensed nurse who either:
As the healthcare industry has changed over the years, the systems that educate our healthcare workers have adapted as well. The number of diploma programs has decreased in recent years, with more associate degree programs, and now bachelor’s degree programs. While each one will lead you to earning your RN license, each one builds on the last.
Completing one of the above programs makes the future nurse eligible to become licensed as a Registered Nurse. For a nurse to get licensed, they must submit an application through their state's board of nursing, and successfully complete the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX) – an exam consisting of a minimum of 75 questions.
Many see RNs as the ‘heavy lifters’ in ERs or hospitals, but their working tasks vary significantly. While some love the adrenaline and varying schedule of working in fast-paced emergency or intensive care units, others opt to work in a calmer, regularly scheduled environment – like a physician’s office, school, or long-term care facility. However, hospitals remain the most common place to work – ranging from smaller local hospitals to large city hospitals with several departments and various specializations and conditions.

What a registered nurse does depends on their specialty, location, training, and experience. But some responsibilities for registered nurses remain universal. According to the American Nurses Association (ANA), the key responsibilities of an RN are:
The above responsibilities will always be a part of a registered nurse's day at any level. However, an RN can also help assess the health of inmates in prisons, answer calls to nursing lines, or work abroad as a travel nurse, commonly on 13-week contracts. They could find themselves doing anything from assisting cancer patients after chemotherapy in an oncology department, to helping deliver babies, or monitoring patients post-surgery.
Some specializations require further certification, experience, or education – such as a BSN qualification.
The Bachelor of Science in Nursing degree, or BSN, is a four-year bachelor’s degree done at a university or college. A BSN degree offers a much broader education than the 2-year associate degree in nursing (ADN) and opens a whole new set of possibilities for a nursing career. The benefits include a higher salary, better job offerings, and an advancement in the job market.
Lately, it’s becoming increasingly more common for healthcare facilities to require BSN degrees for the RNs that they hire. While an associate degree will cover the education and training you need to pass your NCLEX exam and work as an RN, a BSN dives deeper by building on the concepts from the associate degree and taking your skills and education to the next level.
For those who are diploma or associate degree RNs, there are different variations of BSN degree programs for those nurses to reach the next level. These programs - called an RN-to-BSN program, allow RNs without a bachelor’s degree to continue their education and earn the rest of the credits required for the bachelor’s degree. We’ll explore this pathway more in depth later.
The longer study length for a BSN allows nurses to participate in more advanced procedures under a doctor’s supervision, and manage other nurses.
After you've done your BSN, the next steps for even higher positions include the Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) degree, which can prepare you for some of the highest paying nursing jobs. For instance, nurse anesthetists, general nurse practitioners, and mental health nurse practitioners all command a salary of over $100,000 per year.
While there are many pathways to a career in nursing, if you don't have an RN license yet, jumping straight into a BSN will give you a great head start in your nursing career.
A BSN degree is an excellent foundation for any number of nursing-related professional roles and leadership positions. Not only do you receive an extensive education in all critical nursing courses, but the degree also focuses on liberal arts and science, including chemistry, nutrition, anatomy, mathematics, and English – giving a more well-rounded perspective.
A BSN program also focuses on developing skills above and beyond nursing practice, including:
Essentially, it equips nurses with all of the professional skills needed as well as a better understanding of the cultural issues involved in joining this well-respected vocation.
There are many benefits to getting your BSN. As mentioned, being a Registered Nurse with a BSN has two visible advantages to being a non-BSN RN:
But there are many others too.
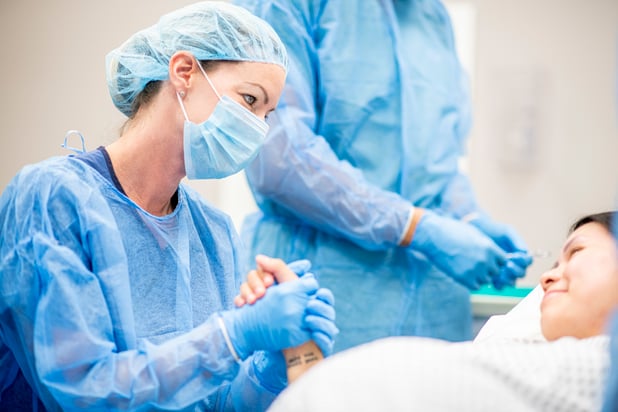
Without a BSN or higher, career advancements can be more difficult for an RN.
But do you need to spend four years full-time in university to get your BSN? The answer is no. It can be lot faster.
If you already have a bachelor’s degree in another field, you can earn your BSN degree in what is called an accelerated BSN program, or second degree BSN program, in 12 - 18 months.
If you’re already an RN through a diploma or associate degree, you can earn your RN to BSN degree online in as little as 12 months – sometimes less – while still working full-time.
Online flexibility means that you can keep your paycheck, knowing that you'll open doors to a higher salary, better knowledge, and more specialized nursing positions in only a year.
But what does it cost? Some colleges allow RNs to transfer credits from previous college coursework in their RN-BSN programs, which can help reduce cost. For the majority of students, this equates to a cost reduction of over $7000. The ability to reduce costs, plus the flexible online format makes RN-BSN online very inexpensive.
Regardless of which pathway you choose, there is financial support available – including scholarships to apply for.
You’ve probably started to understand the difference between RN and BSN. Even though they both lead to a nursing career, the truth is, the two differ quite a lot. But one doesn’t necessarily exclude the other.
To break it down (including the common ADN):
To compare the salary of an RN and BSN, we need to compare them as ADN vs. BSN registered nurses.
The median pay for an RN in the US is $73,300 per year. For both ADN and BSN nurses, starting salaries are quite similar. But the nurse with the BSN has an advantage; they are higher in demand, can leverage their four-year education to get a higher salary, and can work in specialty areas with higher pay.
According to PayScale, the average hourly salary for an RN is $29.62, and $32.20 for nurses with a BSN. This difference equates to a lot per year.
While an ADN and BSN both ultimately lead to the same goal - becoming a Registered Nurse - the two routes have some big differences.
For a thorough, in-depth education in nursing, a higher salary, an easier time finding a job, and the possibility of working in specialized areas, a BSN degree is essential.
If you’re an RN looking to get your BSN degree fast while working full-time, an online RN-to-BSN program is your best, most affordable, and fastest choice.
The bottom line is: you don’t need a BSN degree to become an RN; but in the long-term, it is often well worth the investment.
Is a BSN worth it? Do I need one to become a nurse? What does the career outlook for both paths look like? What are the salary expectations? Find out the answers to these common questions in this blog.

Ready to start a professional career in nursing? You may be wondering how long nursing school is - learn more about timelines, degrees, and job options.
What is a BSN degree & how do I get started? Learn about the types of BSN degrees, what jobs are available in this field, benefits & expected salaries. Get started.
© 2024 Labouré College of Healthcare. All Rights Reserved.
Comments